A Hypervisor is the software that produces and manages virtual infrastructure , allowing multiple operating systems to run and share resources on a single physical machine
Sharing CPU cycles, RAM memory and storage.
The system running the hypervisor is called the host
It is commonly a rack mounted server blade.
The virtual machines running on the host are the guest
Each VM takes one set of physical hw
Multi-tenancy of guests usually involves OS like windows, linux, BSD, etc
| HW |
| Hypervisor |
| Guest OS(s) |
| App(s) |
Some implementations are:
AWS runs on Xen type 1 hypervisors
| HW |
| Host OS |
| Apps, one is a Type2 Hypervisor |
| Guest OS |
| App(s) |
Some implementations are:
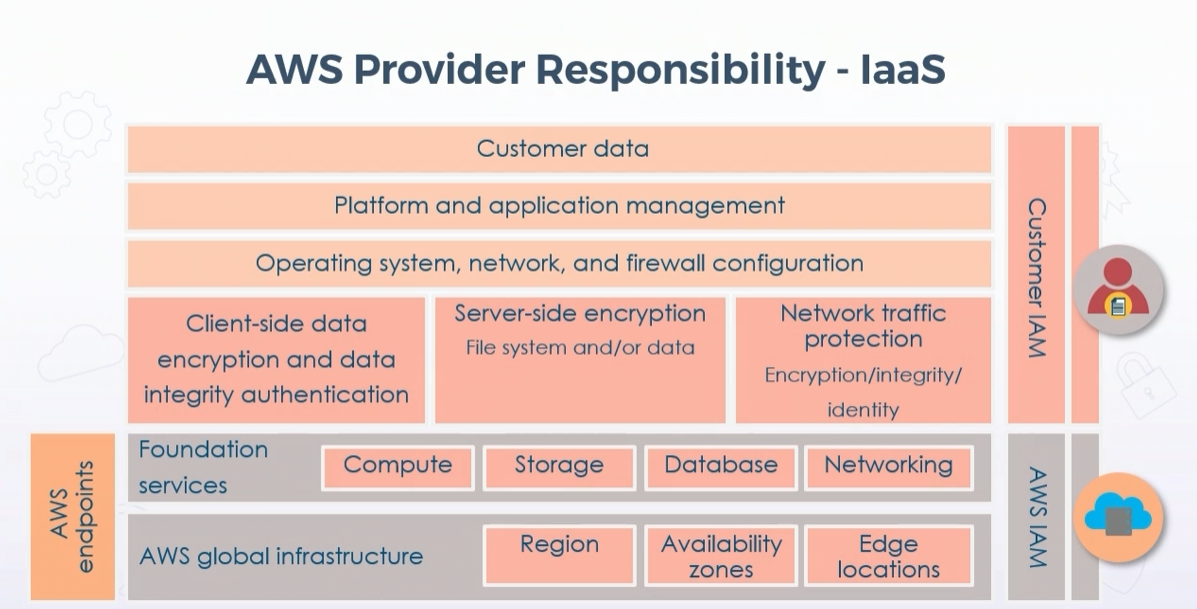
AWS manages physical security and hypervisor security, it ensures guests OS run securely isoletad from one another.
The consumer takes responsability for managing the guest operating system (including updates and security patches), related application security, the design of the virtual networks and logical firewall.
Reduction or Acceptance
How much do you decide to manage or use managed services?
How much is on-premises and how much is on cloud?
Shared responsability is a form of risk transference
When you migrate resources to a cloud services provider (CSP), the service level agreement (SLA) becomes a joint shared responsability between the provider and the consumer
IasS and SaaS have clear demarcation points
PaaS demarcation is less clear, and depend on how managed service means.
AWS responsabilities:

The particular services determines the customer-side responsabilities.
For example with EC2 instances you would be responsible for updates and upgrades and security patching.
The customer is ultimately responsible for compliance, regulations and adhering to attestation and auditing by third parties.
Only the root account can do:
On VPC Dashboard
There are several network resources
There is a default VPC, it uses a 16bit mask, you can have several subnets
You can have many VPCs on your account, Custom VPC is labeled as Non-default VPC
Example: having 3 subnets in your VPC, you can put each one in an availability zone having high availability.
VPC wizard is infrastructure as code: You can use CloudFormation
Ways to configure a VPC:

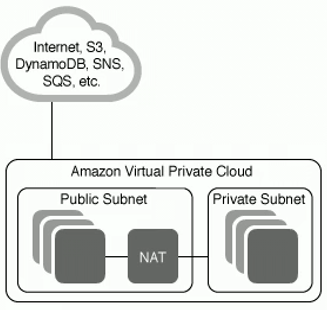

AWS creates a default VPC
For each VPC it creates 3 subnets
You can view the route table for each subnet
If a subnet has configured a IGW (Internet Gateway) it is considered public
If I remove the IGW it becomes a private subnet
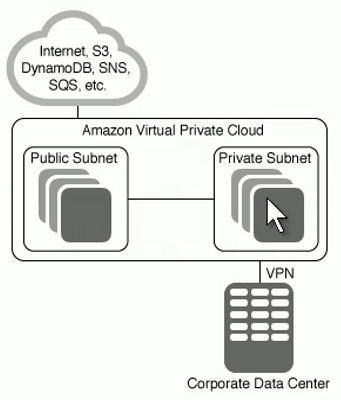
I can add a VPG (Virtual Private Gateway) to connect to a VPN
An Instance can be asigned a public IP address from the IP pool or an Elastic IP address
An Elastic IP address is also taken from the pool, but the beauty is asigned to your account, and you can reallocate to other EC2 instance. If you have a Elastic IP and is not assigned, you will be charged.
To being able to communicate a instance that is only on private subnet, you have to add a NAT gateway, the NAT gateway sits in the public subnet.
By the way, a NAT gw has to use an Elastic IP address. NAT is used only for IPv4.
For IPv6 you need to use an Egress Only Internet Gateway only for IPv6.
DHCP options can be used if you want to modify the default DHCP server.
Endpoints allows you to setup communication between services in the AWS cloud, there are 2 types:
The Interface endpoint will use one of the IP adress in your subnet, while the gateway endpoint is just an entry in the route table.
If you want to connect two VPCs you will do that through Peering Connections it can be done
even between different root accounts, one is the requester and the other is the accepter.
The IP address can not overlap
They are not transitive, that means you have to explicitly create a peer for each pair of VPCs
EC2 - Elastic Cloud Compute
EC2 instance is a provisioned virtual machine, to provision a virtual machine you start from a software stack image or AMI.
There is a AMI marketplace with more than 500 images of different OSs and software stacks.
You can build your own AMI with the EC2 Image Builder, also it can build docker Images.
AMI is a software template which includes OS and optionaly applications.
There is a lot of Linux distributions for everyone like:
For several architectures:
The AMI will include the root volume of that particular OS
In IaaS you will be responsible of licence and software that is installed within the Instance
Will be covered later.
There are several options to connect to the resources in a VPC that is not public: